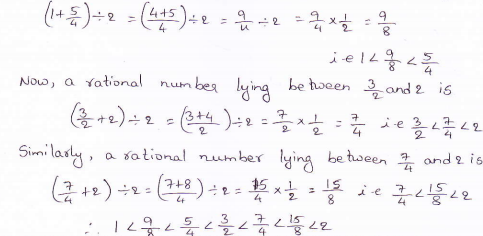Download Formula BookPhysics eBookChemistry eBookBiology eBook
Sources of Energy Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science
PREVIOUS YEARS QUESTIONS
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2015
1.Name any two fossil fuels.
Ans. A good fuel is the one which
- has high calorific value,
- is non-polluting,
- is easy to transport and easily available,
- has moderate ignition temperature.
2.Mention the purpose of blackening the interior of a solar cooker.
Answer. The purpose of blackening the interior of a solar cooker is that the black surface absorbs more heat radiations of incident solar energy (about 98%) as compare to white or other light coloured surface
Short Answer Type Question[ll] [3 Marks] – Year 2015
3.Why do people oppose the construction of Tehri Dam on the river Ganga and Sardar sarover project on the river Narmada. (Or)
Mention three disadvantage of producing hydroelectricity by constructing the dams.(Or)
List any three ways in which construction of dams for production of electricity adversely affects the environment of that place.
Answer.
- Large area is required to build the dam that result rehabilitation of displaced people.
- Large eco-systems are destroyed when submerged under the water in dams.
- The vegetation which is submerged rots under anaerobic conditions and gives rise to large amounts of methane gas which leads to a green-house effect.
4. Reena’s father works with a company that builds dams. Once he took her to the site where a dam was being built. Reena saw a group of people sitting there and shouting slogans against the building of dam. She talked the group of people and asked them about their problems and then discussed it with her father. She then tried to convince the people to talk with the authorities and come to an amicable solution. The discussion was successful. Reena’s father was very proud of his daughter. Now answer the following questions:
(i) Why was Reena’s father proud of his daughter?
(ii)Why was the group of people protesting against the building of dam?
(iii) Reena’s contribution to the peaceful resolution of the conflict proved to boon for many citizens of the country. How?
Answer.
(i) Because she convinced the people by explaining them the advantage of constructing dam and come with a solution of rehabilitation of displaced peoples. So the contribution to the peaceful resolution of the conflict make Reena’s father proud of his daughter.
(ii)The group of people protesting against the building of dam because of following disadvantages
(a) A large area of agricultural land and human habitation are sacrificed as it get submerged at the dam site.
(b) Large ecosystems are destroyed when submerged under water.
(c) The decomposition of vegetation under anaerobic condition produces methane gas which is also a greenhouse gas.
(iii)(a) The citizens are not affected by flood as it can be controlled by storing the water behind the dam.
(b) Farmers get benefited as water for irrigation is available for the whole year.
(c) Low cost of production of electricity gives monetary gain which is a boon to citizens.
5.Bio gas is an excellent fuel. Justify the statement by giving two reasons. Mention the main constituents of bio gas along with its percentage.
Answer.
(i) It burns without smoke and leave no residue therefore causes no atmospheric pollution.
(ii)Its heating capacity is high, i.e. it has high calorific value. Main constituents of bio gas: The composition of bio gas varies depending upon the nature of organic matter feeding in’the digester and advanced waste treatment technology. The typical composition of bio gas is
Methane 50 – 75%
Carbon dioxide 25 – 50%
Nitrogen 0 – 10%
Hydrogen 0 – 1%
Hydrogen sulphide 0 – 3%
6.(a) Define tidal energy.
(b) Explain how the tidal energy is harnessed and write one limitation of the use of tidal energy.
Answer.
(a) Tidal energy: The energy produced by the surge of ocean water during high and low tides due to difference in sea-levels is called tidal energy. The high and low tides occur due to the gravitational pull of the moon. This causes enormous movement of water.
(b) Tidal energy is harnessed by constructing a dam near the shores. During the high tides water flows into the dam and during the low tides, water flows out. This flowing water rotates the turbine, present at the opening of the dam and produces electricity.
7. Define process of nuclear fission. Writ the steps involved in generating electricity in a nuclear reactor.
Answer. Nuclear Fission: The process in which a heavy nucleus (such as uranium, plutonium or thorium) is broken into two nearly equal fragments when bombarded with low-energy neutrons and a tremendous amount of energy is released. This process is called nuclear fission.
Steps involved in generating electricity:
- The fuel rods full of uranium pellets are placed in a nuclear reactor chamber.
- Low-energy neutrons are bombarded on uranium fuel rod.
- A self-sustaining fission chain reaction starts that releases energy at a controlled rate.
- With this heat the reactor converts water to steam at a high temperature and pressure.
- This high temperature and pressure steam spins generator turbines producing electricity.
- The steam cools back into water, which can then be used over again.
Long Answer Type Question [5 Marks] – Year 2015
8.Nikhil and Neha went to a remote village in Kerala to meet their grandmother. They were surprised to see a biogas plant in Mr. Nair’s house in the neighbourhood. There were plenty of livestocks and the household used cooking gas from the plant. Also their farms had rich vegetation. They contacted sarpanch of the village and convinced him to set up a biogas plant for village community.
(a) Mention the values displayed by Mr. Nair, Nikhil and Neha.
(b) Explain the possible arguments given by Nikhil and Neha to the sarpanch to convince him to set up community biogas plant.
Answer.
(a) Mr Nair: Higher degree of general awareness, helping nature.
Nikhil and Neha: Knowledge sharing.
• helping nature.
• concern for community advantage.
(b) Possible arguments given by Nikhil and Neha in favour to set up community biogas plant, to the sarpanch on
- Economical source of energy.
- Cleanliness of the whole village.
- Use of slurry left behind as mannar which is rich in nitrogen and phosphorous.
- It reduces air pollution and greenhouse effect.
- It raises the standard of living.
- It is beneficial to entire village community. Basically they discuss and explain the advantages of community bio gas plant for the’entire village.
9.Solar cooker takes more time as compared to the LPG to boil potato or rice, yet Kunal uses solar cooker for such type of cooking:
(i) Why does Kunal uses Solar cooker instead of LPG? Give reasons for your answer.
(ii) Name the phenomenon which is responsible for obtaining high temperature in solar cooker.
Answer.
(a)(i) There are no energy losses while cooking on the solar cooker as the food gets cooked in a controlled environment whereas cooking on the LPG leads to maximum percentage of energy loss.
(ii) Temperature controlled cooking retains the nutrient value of the food.
(iii) Using the solar cooker, LPG can be served which result reduction in the emission of CO2.
(iv) It saves a lot of prestigious time which is normally consumed for cooking purpose.
(b) Greenhouse effect.
10. Manoj’s father works in a nuclear power reactor. He asked his father to take him for a visit to nuclear power reactor. But his father was not keen to take him there. Now answer the following questions:
(i) What could be the possible reason of Manoj’s father not taking him to the nuclear power reactor?
(ii) Write one advantages and one disadvantage of setting up a nuclear power reactor. .
Answer.
(a) (i) Safety concerns.
(ii) Health concerns.
(b) Advantage: From a small amount of nuclear fuel, a large amount of energy is released in a nuclear power reactor.
Disadvantage: There is risk of harmful radiation leakage from nuclear waste.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2014
11. Name the part of a biogas plant where reactions take place in the absence of oxygen.
Answer. Digester chamber.
12. Name the kind of energy possessed by wind and the device used to harness it.
Answer. Kinetic energy, wind mill.
13. List two non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer. Geothermal, solar, biomass, water, wind are the non-conventional sources of energy, (any two)
14. A black surface absorbs more heat radiations as compared to a white or a
reflecting surface under identical conditions. List two solar devices which make use of this property in their design.
Answer. Solar cooker, solar water heater.
15. Name any two elements that are used in fabricating solar cells.
Answer. Germanium, Silicon.
16. Why a solar cooker painted black form outside?
Answer. Black surface absorbs more heat as compared to white or reflecting surface under identical conditions.
Short Answer Type Question [I] [2 Marks] – Year 2014
17. Define fuel. List any two characteristics that you would look for in a good fuel.
Answer. A substance that produces useful energy when it burn or undergoes a chemical f or nuclear reaction. The fuel such as coal, wood, oil, or gas provides energy when burned. A good fuel is the one which produces a huge amount of heat on burning. It does not produce a lot of smoke and is easily available.
Short Answer Type Question[ll] [3 Marks] – Year 2014
18 State any three reasons to justify that LPG is considered as an ideal fuel.
Answer. LPG is considered as an ideal fuel because
- It is easy to store, handle and transport.
- It produces large amount of heat on burning.
- It does not leave any residue on burning,
19 Sate any three advantages of charcoal over wood.
Answer. Advantages of charcoal over wood
- It has higher calorific value, i.e. higher heat generating efficiency.
- Charcoal does not produce smoke on burning so it is a clean fuel.
- It is easier to transport and ready to use in a convenient dry and broken-up form.
20. Ramesh is a student of standard X. He organized many activities in his school to convey the students about the various advantages and disadvantages of using renewable and non-renewable sources of energy. Many students of the school took part and concluded about the best choices of energy sources on this basis.
Answer the following questions:
(i) What activities Ramesh might have had assigned for the students?
(ii) Name any two renewable sources of energy.
(in) Which two values are reflected in Ramesh’s thought and action?
Answer.
(i) Activities that Ramesh have had assigned for the students are:
(a) Hands on projects related to renewable and non-renewable sources of energy.
(b) Photograph exhibitions on the topic “use of fossil fuel and its impact on the environment.”
(c) Essay writing competition on a “renewable energy technology that could potentially be used for community.”
(d) Group discussion on advantages and disadvantages of using renewable and non-renewable sources of energy for selection of best source of energy.
(ii) Solar energy, hydro energy.
(iii) Ramesh’s thought: Higher degree of general awareness proper use of renewable source of energy.
Ramesh’s action: Concern for community advantage and good management.
21. Megha asked her mother to install a solar water heater on the roof top. Her mother asked about the need of such installation. Megha convinced her mother and succeeded in setting up a solar water heater on her roof top.
(i) State one advantage of installing the solar water heater to Megha’s family and to the society.
(ii) What qualities of Megha are reflected in her action?
(iii) State one limitation in using solar water heater.
Answer.
(i) Advantage of solar water heater (any one)
(a) Once solar water heater installed, the family and society never need to pay for heating up the water again.
(b) Megha’s family and society make their contribution to the nation to curb the emission of green house gases.
(ii) General awareness, concern for community advantage and proper use of ‘ renewable source energy.
(iii) (a) It does not work at night as well as on cloudy day.
(b) Relatively low heating system efficiency of passive solar water.
22. Mariyam made a solar cooker on her own. She used a white metallic box with a lid. She put the food in the solar cooker for heating and closed the lid. But she did not get good results. She then consulted her teacher to know her mistakes. Her teacher pointed out her mistakes, which she later rectified.
(a) According to you, which two mistakes were made by Mariyam and what
did she do to rectify them?
(b) Which qualities of Mariyam are rectified in her action.
answer.
(a) The possible mistakes were made by Mariyam are:
- The outer and interior of solar cooker might not have been blackened.
- Instead of using glass lid she might have been used plastic cover.
- The solar cooker might not have been insulated properly.
- The cooker utensil used for cooking might not have been blackened.
(b) • Gaining practical knowledge of what she have learned in theory. She wanted to adopt the eco-friendly life style.
23. Aditya suggests his family to install a solar water heater at their residence. But
some of the family members were in favour of installing an electric geyser.
Ultimately the family got water heater installed.
(a) Which according to you was correct? Give two reasons in support of your answer.
(b) Mention two possible changes in the thinking of the family members
because of the arguments Given by Aditya.
answer. (a) The decision of installing the solar water heater was correct this is due to
(i) Their system use solar energy which is a renewable source of energy and free.
(ii)It will reduce our dependence on fossil fuel, improving on our energy security and reduce the country import bill for fuel.
(b) Two possible changes in the thinking of the family members because of the arguments given by Aditya are:
(i) We should conserve the non-renewable fuels for application for which renewable source of energy is not easily available.
(ii)Solar water heating is good investment and cost effective. It is one of the safe and efficient way to deliver hot water free of cost.
24. Traffic jams, outside the school gate was a common sight since most of the students came on their own cars. This became a topic for discussion on every P.T.A meeting. On one such P.T.A meeting, the principle pointed out the examples of four of their teachers who were carpooling for the past several
years. She asked the parents to adopt this method to sort out the problem.
(i) List two values shown by the teachers mentioned by the principal.
(i) Explain two advantages that will occur if more parents emulate the examples of these teachers.
answer.
(a) The two values shown by the teachers mentioned by the principle are:
(i) Eco-friendly life style.
(ii) Co-ordination and friendship.
(b) (i) Reduction in air pollution and traffic congestion: Car pooling reduces the emission of CO2 into the atmosphere as every car pooling participant takes another car off the road.
(ii) Save money: Car pooling saves money by using less fuel. It reduces the cost involved in repetitive or long distance journey.
25. On returning home, Neha, a IXth std. student noticed that her 6 years old brother Neresh, watching T.V in the afternoon with all the lights and fans ‘on’. She noticed that the windows were closed and curtains were drawn, which made the room dark, so, Naresh had put on the lights. She calmly opened the windows, drew the curtain aside, which illuminated and aerated the room. Then she made Naresh put “off” the lights and made him understand the reason behind her action. (Assume that they are getting electric supply from Thermal Power Plant)
(a) List the two value exhibited by Neha.
(b) Explain how she tried to give same values to her brother.
answer.(a) The values exhibited by Neha are:
(i) Responsible citizen in the conservation of energy resources.
(ii) Adopt fuel and money saving technique in her life.
(b) Neha tried to give the same values to her brother Naresh by opening the windows, draw the curtain aside, which illuminated and aerated the room. This way she shows the practice of adopting renewable sources of energy like solar energy and conserve the fossil fuel like coal.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2013
26. What is acid rain?
answer. Acid rain: The rain containing the acidic oxides such as oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur.
27.Write the name of the substance whose vapours are used to run the turbine of the generator of ocean thermal energy plant.
answer. Ammonia.
28. Mention the minimum temperature difference required between surface water and water at a depth of upto 2 km in an ocean thermal energy plant.
answer. 20 °C or 293 K in trapping geothermal energy
Short Answer Type Questions [II] [3 Marks] – Year 2013
29. Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable sources of energy. Also give an example of each of these sources.
answer.
Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.
30. State the principle of working of ocean thermal energy conversion plant.
Explain how the plant works? Write one essential condition for it to operate
properly.
answer. Principle of working of OTEC: The water at the surface of the ocean is warmer
than the water at deeper depths. This temperature difference can be used by
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) systems to generate electricity.
Working of OTEC:
- In OTEC plant, the energy of warm surface water is used to convert low i boiling point liquid ammonia into gaseous state.
- The vapour of ammonia at high pressure is used to spin the turbines of generators converting the Ocean thermal energy to electricity.
- The used vapour pass through the condenser where cold water, pumped from the deeper parts of ocean condenses ammonia vapour back into a liquid.
- This process is repeated again and again ,to get continuous production of electricity.
Essential condition for it to operate properly: The temperature difference between the warmer water at the surface and colder water at depths up to 2 km should be 293 K (20°C) or more.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2012
31.Name one fuel used in nuclear reactor.
answer. Uranium-235.
32.Name any two elements that are used in fabricating solar cells.
answer. Germanium, Silicon.
33.Name the reaction responsible for large energy production in the sun.
answer. Nuclear fusion.
Short Answer Type Questions [II] [3 Marks] – Year 2012
34.Mention why is it not possible to make use of solar cells to meet all our energy needs? State three reasons to support your answer. Also mention three uses of solar cells.
answer. It is not possible to make use of solar cells to meet all our energy needs because:
(i) of limited availability of special grade semiconducting materials such as silicon and germanium.
(ii)solar cells have lower efficiency as they depend entirely on intensity of solar radiation.
(iii) the process of manufacturing of solar cells is very expensive, silver used for interconnection of cells in the panel further adds to the cost.
Uses of solar cells:
(i) They provide electric power to satellites and space probes.
(ii) They provide electric power to off-shore drilling platforms and light houses.
(iii) TV relay stations or wireless transmission systems located in remote areas use solar panels to get electric power.
35.Out of two elements A and B with mass number 2 and 235 respectively, which one is suitable for making ,
(a) a nuclear reactor,
(b) a hydrogen bomb?
Name the nuclear reaction involved in each case. Write one difference between the two types of nuclear reactions.
answer.
(a) For a nuclear reactor— element ‘B’ with mass number 235 is suitable as a fuel in a nuclear reactor.
(b) For a hydrogen bomb— element ‘A’ with mass number 2 is suitable for making the hydrogen bomb.
The nuclear reaction involved in
(a) nuclear reactor is nuclear fission reaction and
(b) nuclear bomb is nuclear fusion reaction.
Difference between fission and fusion:
Fusion reaction releases much greater energy with non-radioactive products than the energy released in fission reaction with radioactive products.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2011
36. List two nutrients that the slurry left behind in the biogas plant contain.
answer. Nitrogen and phosphorous.
37. Biogas is also known as gobar gas. Justify.
answer. Starting material for biogas is mainly cow dung. So, it is also known as gobar gas.
38. List two practical uses of biogas in rural areas.
answer. Practical uses of biogas in rural area are:
- It is an excellent fuel which burns without smoke with high heating capacity.
- It is also used for lighting.
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] – Year 2011
39. Bio gas is considered to be a boon to the farmers. Give reasons.
answer.
- It is the source of excellent manure, rich in nitrogen and phosphorous which
can be obtained from the biogas plant in addition to biogas. - It provides the safe, efficient and profitable disposal method for bio-waste and sewage material.
40. What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
answer. Advantages of nuclear energy are:
- A small quantity of nuclear fuel is needed to produce a large amount of useful energy.
- Nuclear power plant produces less atmospheric pollution than thermal power plants, if the nuclear fission reaction is performed properly.
- Small amount of nuclear fuel can run a nuclear power plant over a long period of time. There is no need of inserting the nuclear fuel in the nuclear reactor again and again in a short period as in case of thermal power plant.
41. What is a solar cell panel? Mention any three of its applications.
answer. A large number of solar cells combined in an arrangement to obtain large electrical power is called solar cell panel.
Applications of solar cell panel are:
It provides the electric power for the:
- working of artificial satellites stationed in outer space,
- running of irrigation water pumps by the farmers in rural areas,
- street lighting in remote areas.
42. Out of two solar cookers, one was covered with a plane glass slab and the other was left open. Which of the two solar cookers will be more efficient and why?
answer. The solar cooker which was covered with a plane glass slab would be more efficient. The glass lid allows the heat radiation from sun to enter the solar cooker but does not allow the reflected heat radiation to escape or go outside the box. Thus, heat trapped inside the box increases the temperature. Glass lid also reduces heat loss due to reflection.
Short Answer Type Questions [II] [3 Marks] Year 2011
43.List any three hazards of nuclear waste. How does the disposal of nuclear waste pose a problem for the plant and animal life?
answer. Hazards of nuclear wastes are:
- Nuclear waste contains radioactive substances which emit harmful nuclear radiations.
- There is a high risk of environmental contamination.
- It is highly toxic.
Effect of nuclear waste on plant and animal life is:
The radiations emitted from the nuclear waste penetrate deep inside the human or animal body where they can damage biological cells thereby initiate cancer or causes genetic disease.
Increased mortality of plants, soil invertebrates and mammals and reproductive losses in plants and animals have also been observed.
44. (a) Charcoal is a better fuel than wood. Why? .
(b) How does biogas plant help to reduce the problem of pollution?
answer.
(a) Charcoal is considered to be a better fuel than wood because:
- It burns without flames.
- It is comparatively smokeless.
- It has higher calorific value, i.e. higher heat generating efficiency than wood.
(b) Biogas plant helps to reduce the problem of pollution in the following ways.
- It provides better sanitation due to safe disposal of bio-waste and sewage material.
- Biogas obtained from this plant produces less smoke on burning. (Hi) The residue left can be used as a manure which can be used as an alternative
of fertilizers. Thus, it prevents soil and water from degradation.
45. (a) What is geothermal energy?
(b) What are the advantages of wind energy?
answer.
(a) The heat energy obtained from the molten rocks formed in the deeper hot regions inside the earth are called geothermal energy.
(b) Advantages of wind energy are:
- It is an inexhaustible source of energy.
- It does not cause any environmental pollution.
- It is available at free of cost.
46. (a) How does construction of dams across the river get linked with production of greenhouse gases?
(b) How do technological inputs improve the efficiency of biomass fuels?
answer.
(a) A vast variety of plants get submerged in water, rot under anaerobic conditions and produce large amount of greenhouse gases such as methane.
(b) Traditional uses of biomass fuels are not only efficient but they also produce a lot of pollutants which are hazardous to health. Therefore, technological inputs are necessary to improve the efficiency of these fuels and make them environment friendly. With the help of technology, smokeless chulhas and biogas plants have been designed.
Short Answer Type Questions [2 Marks] -Year 2010
47. Mention any four limitations in harnessing wind energy on a large scale.
answer. Limitations in harnessing wind energy are:
- Speed of wind is not available at all time and at all places.
- To establish the wind energy farm, a large area of land is needed.
- Speed of wind should be higher than 15 km/h to harness the wind energy.
- Construction of windmill and its installation is very expensive.
48. What happens when wood is burnt in a limited supply of oxygen? Name the residue left behind after the reaction and state two advantages of using this residue as a fuel over wood.
answer. When wood is burnt in a limited supply of oxygen, volatile materials present in it get removed and cooled to get wood tar and wood gas.
The black residue left behind aftqr the reaction is known as charcoal. Advantages of using charcoal as a fuel over wood are:
- Burning of charcoal does not produce smoke. On the other hand, wood produces a lot of smoke on burning.
- For a given quantity, charcoal produces ,more heat than wood.
49. Name four gases commonly present in biogas. State two advantages of using this gas over fossil fuels.
answer. Methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide.
Advantages of using biogas over fossil fuels are:
- Biogas burns without smoke, leaves no residue unlike coal.
- Biogas is cheaper as compared to fossil fuels.
50. How are the wastes produced in nuclear power plants different from those produced in a thermal power plants ? What happens to the waste of a nuclear power plant?
answer.The waste obtained from nuclear power plants is highly radioactive in nature which emits harmful radiations, whereas waste produced in a thermal power plant is non-radioactive.
Management of nuclear waste is given as follows:
- Some products of nuclear waste are buried in sealed steel/lead containers for a long term storage, buried under the ground or dumped in vacated coal mines.
- Other waste products transforms into less harmful products or to products with a shorter half life.
Short Answer Type Questions [2 Marks] -Year 2009
51. In a solar cooker, the following arrangements are made. Write one function of each arrangement.
(a) The box is made of insulating material such as plastic or wood.
(b) The inner walls of the box are painted black.
(c) The box is covered with a transparent glass sheet.
(d) A plane mirror is hinged at an angle at the top of the box.
answer.
(a) To avoid loss of heat from solar cooker to the surroundings.
(b) Black surface absorbs more heat radiations of incident energy.
(c) Transparent glass sheet does not allow the reflected heat radiation to go outside the box.
(d) To increase the amount of solar energy incident on the transparent glass sheet.
52. Describe how hydro energy can be converted into electrical energy. Write any
two limitations of hydro energy.
answer. Conversion of hydro energy into electrical energy
- High rise dams are constructed on the river to obstruct the flow of water to collect it at a suitable height. The stored water has a lot of potential energy.
- The water from a suitable height is allowed to fall on the blades of a turbine located at the bottom of a dam through a pipe.
- Kinetic energy of flowing water rotates the turbine rapidly. Rotation of turbine helps the armature coil of generator to rotate rapidly in the magnetic field. Thus, hydroelectricity is generated.
Limitations of hydro energy:
(i) All river-sites are not suitable for construction of dams.
(ii) Large ecosystems are destroyed when submerged under the water in dam.
Important QuestionsNCERT SolutionsSample PapersNCERT Exemplar Solutions
The post Sources of Energy Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science appeared first on Learn CBSE.